How to Create an E-Commerce website with Python Django
FREE Online Courses: Elevate Your Skills, Zero Cost Attached - Enroll Now!
E-commerce is now part of our daily life, we use e-commerce websites to order anything and everything. Did you ever wonder if we can develop one on our own?
It sounds complex but it’s actually not, we can create an e-commerce website very easily using python django.
Django is an open-source python framework, which is widely used to create web development projects because of its inbuilt functionalities and rapid development.
Project Prerequisites
We will use the following technologies:
Front-end technologies:
- HTML: displays content on web page
- CSS: creates beautiful styles
- Bootstrap: html, css, and javascript framework used to build responsive websites.
Back-end technologies:
- Python: programming language.
- Django framework: web development framework
To install Django, you can use the pip installer from cmd/terminal.
pip install Django
Download Ecommerce Python Code
Please download the source code of python e-commerce website: Ecommerce Website Python Code
Steps to Create an Ecommerce website with Python Django
Let’s create an ecommerce website with python django
1. Starting project:
First of all, we have to create a project and an app. Commands to start the project and app
django-admin startproject OnlineShopping cd OnlineShopping django-admin startapp website
2. Writing Models
Code:
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# Create your models here.
class Customer(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
user = models.OneToOneField(User, null=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
date_created = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
image = models.ImageField(null=True,blank=True)
description = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Order(models.Model):
product = models.ForeignKey( Product,null=True, on_delete=models.SET_NULL)
customer = models.ForeignKey(Customer,null=True, on_delete=models.SET_NULL)
date_ordered = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
status = models.CharField(max_length=20,default= 'PENDING')
def __str__(self):
return self.name
We have used Django’s default database i.e. Sqlite3. We have created three models in this file.
- Product: This model stores product details like image, name, description.
- Customer: Model stores customer details.
- Order: This model stores order related details like buyer’s information, product’s information, date ordered, and the status of the order (pending, packed, delivered, canceled, etc)
To apply the database changes, run the following
Py manage.py makemigrations Py manage.py migrate
3. forms.py
Code:
from django.forms import ModelForm
from .models import *
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class createuserform(UserCreationForm):
class Meta:
model=User
fields=['username','password']
class createorderform(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model=Order
fields="__all__"
exclude=['status']
class createproductform(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model=Product
fields='__all__'
class createcustomerform(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model=Customer
fields='__all__'
exclude=['user']
To implement the crud functionality i.e for creating, updating or deleting entries from the database, we are creating these forms.
4. admin.py
Code:
from django.contrib import admin from .models import * # Register your models here. admin.site.register(Customer) admin.site.register(Product) admin.site.register(Order)
We have written this code to register the models on the admin panel. Now we need a user to access the admin panel, therefore we will create a superuser. Enter your name, email and password to create the same.
py manage.py createsuperuser
5. settings.py
As we are using images in our project we have to update the static path settings in the setting.py file. Append the below code in settings.py
import os
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS=[
os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static')
]
6. urls.py
In this file also we need to specify a static folder path. So, your urls.py should contain the following code.
Code:
"""OnlineShopping URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/http/urls/
Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls'))
"""
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from website.views import *
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('',home ,name='home'),
path('placeOrder/<str:i>/',placeOrder,name='placeOrder'),
path('login/', loginPage,name='login'),
path('logout/', logoutPage,name='logout'),
path('register/', registerPage,name='register'),
path('addProduct/', addProduct,name='addProduct'),
]
urlpatterns+=static(settings.MEDIA_URL,document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
7. views.py
Code:
from django.shortcuts import redirect,render
from django.contrib.auth import login,logout,authenticate
from .forms import *
from django.http import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def home(request):
products = Product.objects.all()
context = {
'products':products
}
return render(request,'website/home.html',context)
def placeOrder(request,i):
customer= Customer.objects.get(id=i)
form=createorderform(instance=customer)
if(request.method=='POST'):
form=createorderform(request.POST,instance=customer)
if(form.is_valid()):
form.save()
return redirect('/')
context={'form':form}
return render(request,'website/placeOrder.html',context)
def addProduct(request):
form=createproductform()
if(request.method=='POST'):
form=createproductform(request.POST,request.FILES)
if(form.is_valid()):
form.save()
return redirect('/')
context={'form':form}
return render(request,'website/addProduct.html',context)
def registerPage(request):
if request.user.is_authenticated:
return redirect('home')
else:
form=createuserform()
customerform=createcustomerform()
if request.method=='POST':
form=createuserform(request.POST)
customerform=createcustomerform(request.POST)
if form.is_valid() and customerform.is_valid():
user=form.save()
customer=customerform.save(commit=False)
customer.user=user
customer.save()
return redirect('login')
context={
'form':form,
'customerform':customerform,
}
return render(request,'website/register.html',context)
def loginPage(request):
if request.user.is_authenticated:
return redirect('home')
else:
if request.method=="POST":
username=request.POST.get('username')
password=request.POST.get('password')
user=authenticate(request,username=username,password=password)
if user is not None:
login(request,user)
return redirect('/')
context={}
return render(request,'website/login.html',context)
def logoutPage(request):
logout(request)
return redirect('/')
Explanation:
Home:
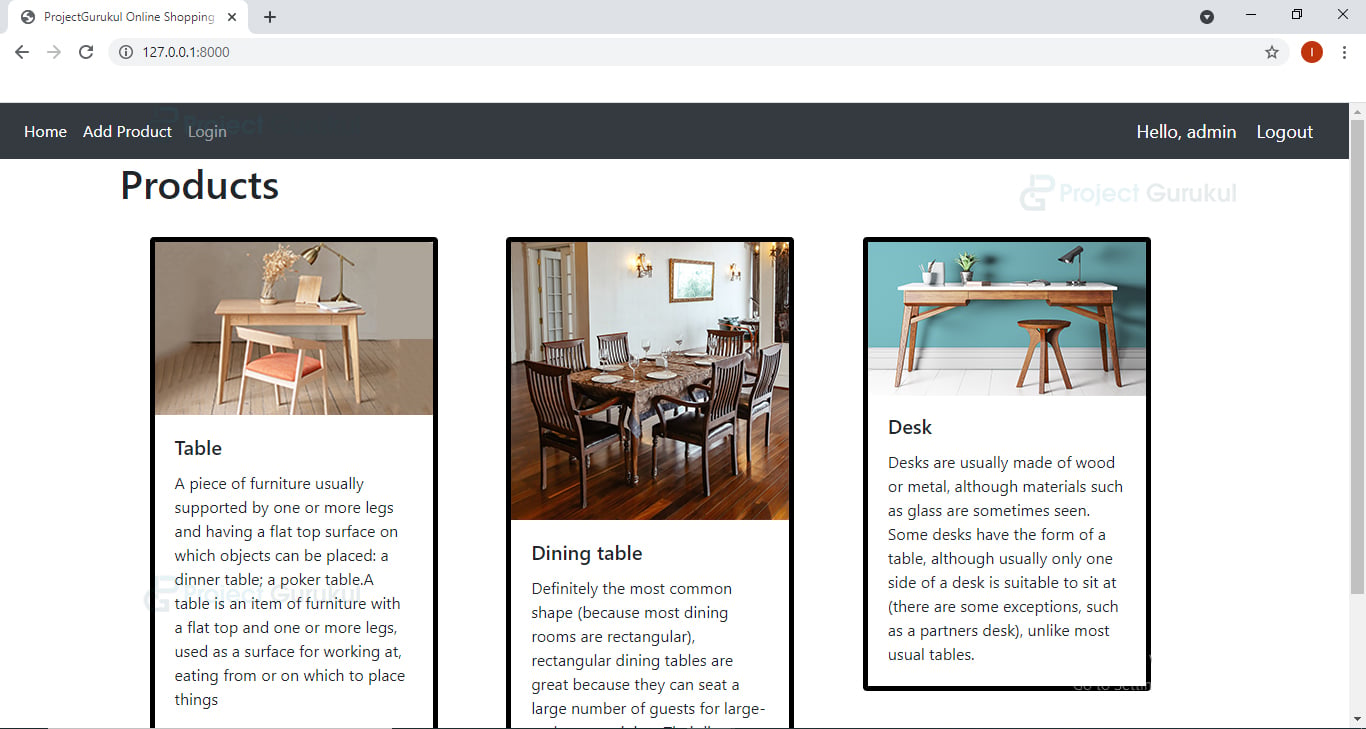
This method provides home page code for both customer and admin, we will just display the available products on the python e-commerce home page and the difference would be only in the navbar for admin and customer.
placeOrder:
This view is a customer-only view and it allows customers to place their orders. It uses the Create Order form to implement its functionality.
AddProduct:
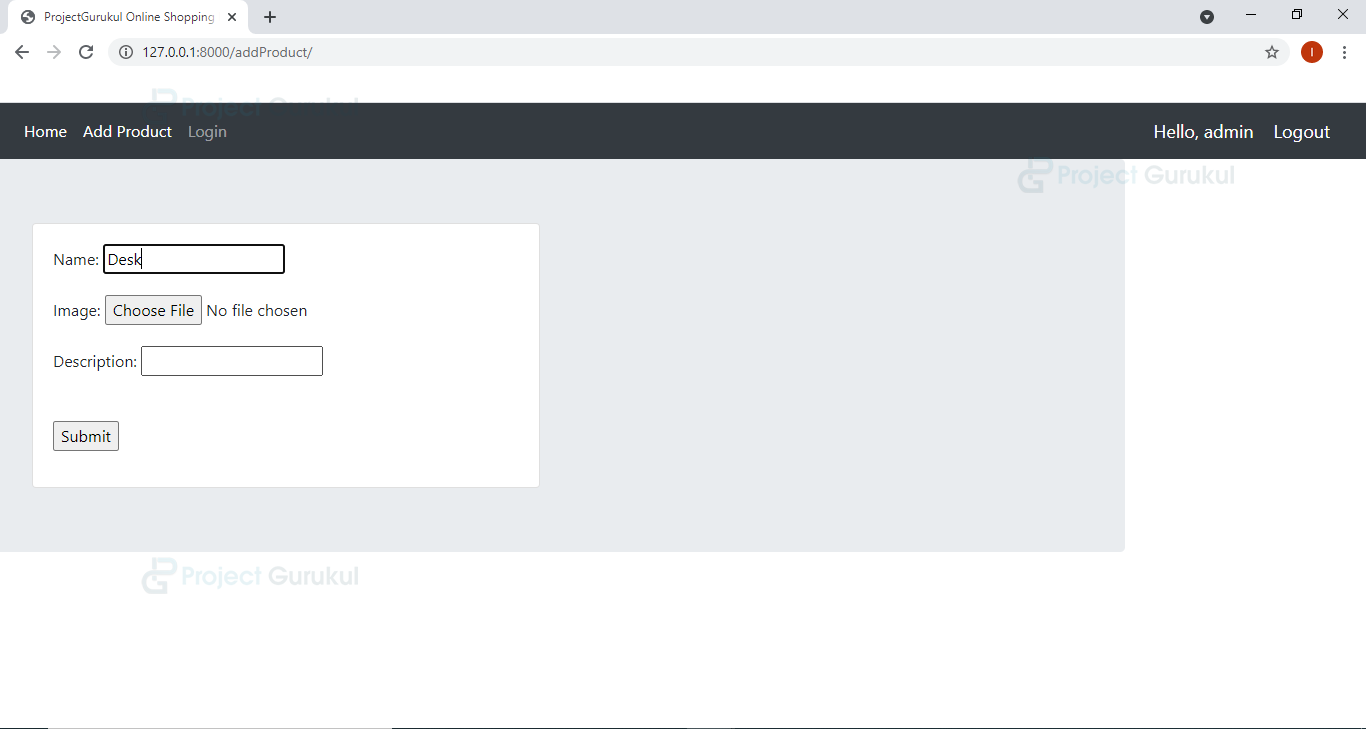
We are using the Create Product Form in this view function, and after validating the information we are storing the product’s details in the database. Note this is an admin’s functionality only.
Apart from these three methods, we have following methods in python e-commerce project: register, login, and logout methods. To implement these methods we have used Django’s inbuilt methods
Logout:
We are just using the logout method in this view.
Login:
We are using the login and authenticate method in the view.
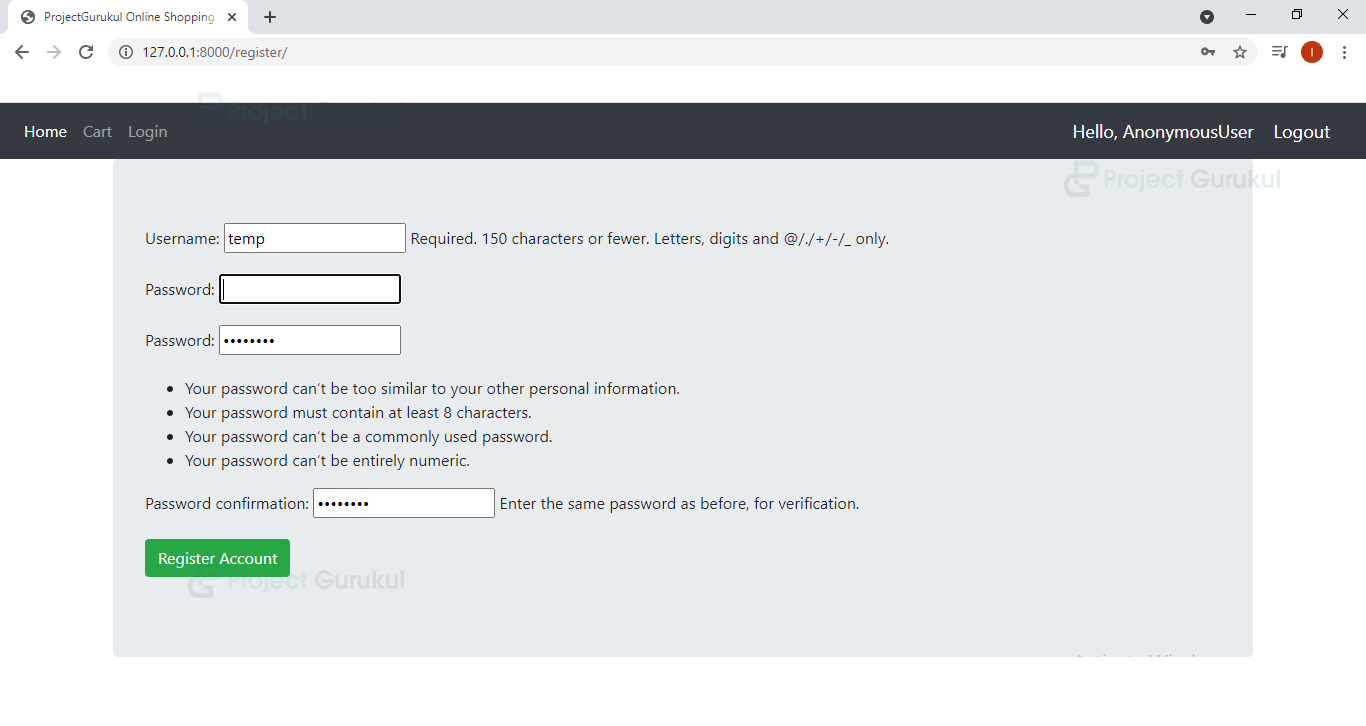
Register:
In this view, we are using two forms: user creation form (to create a user) and a create customer form (to create a customer) and then we are validating the information of both the forms using is_valid method and finally we are adding a new user and a new customer in the database.
8. templates
dependencies.html
{% load static %}
<html>
<head>
<title>
ProjectGurukul Online Shopping Project
</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-9aIt2nRpC12Uk9gS9baDl411NQApFmC26EwAOH8WgZl5MYYxFfc+NcPb1dKGj7Sk" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body>
{% include 'website/navbar.html' %}
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
<br>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-DfXdz2htPH0lsSSs5nCTpuj/zy4C+OGpamoFVy38MVBnE+IbbVYUew+OrCXaRkfj" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-Q6E9RHvbIyZFJoft+2mJbHaEWldlvI9IOYy5n3zV9zzTtmI3UksdQRVvoxMfooAo" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.0/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-OgVRvuATP1z7JjHLkuOU7Xw704+h835Lr+6QL9UvYjZE3Ipu6Tp75j7Bh/kR0JKI" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</body>
</html>
home.html
{% extends 'website/dependencies.html' %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container ">
<h1>Products</h1>
<div class="card-columns" style="padding: 10px; margin: 20px;">
{% for p in products%}
<div class="card" style="width: 18rem; border:5px black solid">
<img class="card-img-top" src="{{p.image.url}}" alt="Card image cap">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{p.name}}</h5>
<p class="card-text">{{p.description}}</p>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% endblock %}
navbar.html
{% load static %}
<style>
.greet{
font-size: 18px;
color: #fff;
margin-right: 20px;
}
</style>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNav" aria-controls="navbarNav" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNav">
<ul class="navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'home' %}">Home</a>
</li>
{% if request.user.is_staff %}
</li>
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'addProduct' %}">Add Product</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="nav-item">
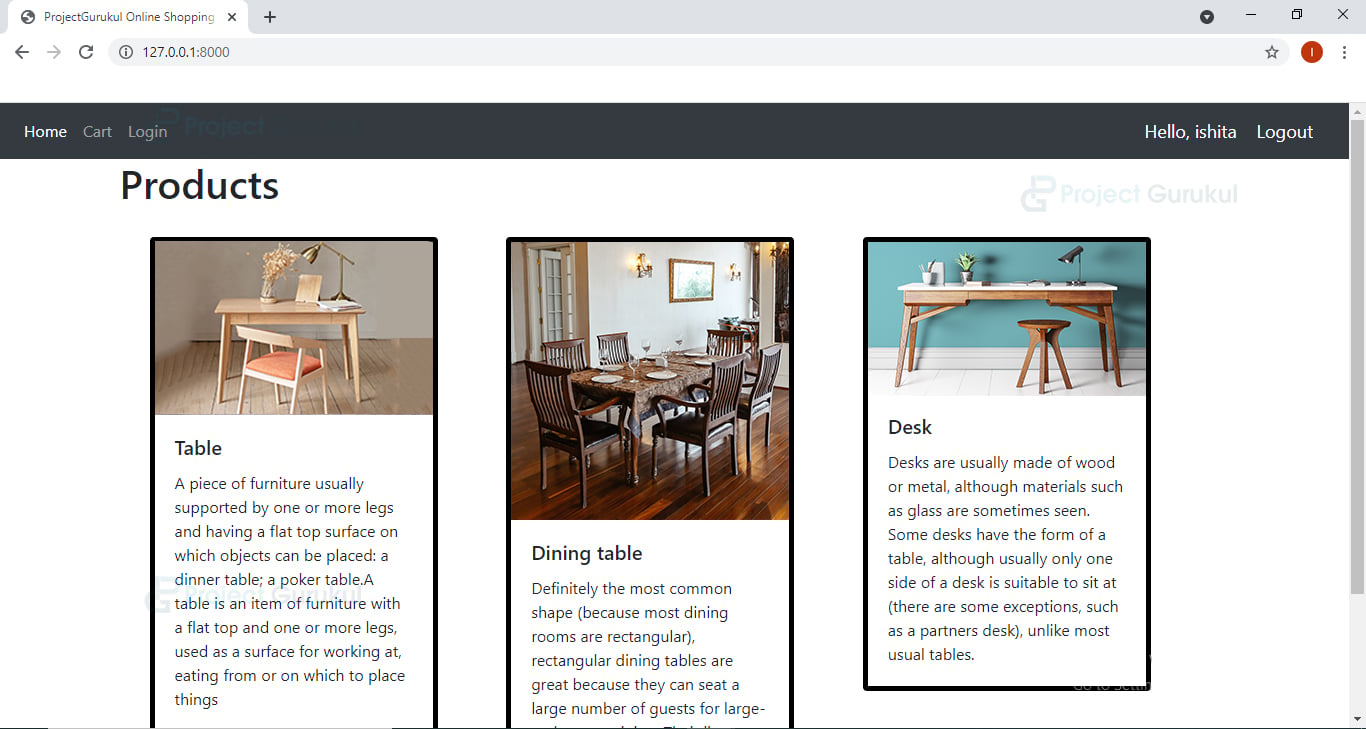
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'placeOrder' request.user.customer.id %}">Cart</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'login' %}">Login</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<span class="greet">Hello, {{request.user}}</span>
<span ><a class="greet" href="{% url 'logout' %}">Logout</a></span>
</nav>
addProduct.html
{% extends 'website/dependencies.html' %}
{% block content %}
<div class="jumbotron container row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="card card-body">
<form action="" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %}
{{form.as_p}}
<br>
<input type="submit" name="submit">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
placeOrder.html
{% extends 'website/dependencies.html' %}
{% block content %}
<div class="jumbotron container row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="card card-body">
<form action="" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %}
{{form.as_p}}
<br>
<input type="submit" name="submit">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
register.html
{% extends 'website/dependencies.html' %}
{% load static%}
{% block content %}
<div class="container jumbotron">
<form method="POST" action="" >
{% csrf_token %}
{{form.as_p}}
{{customerform.as_p}}
<input class="btn btn-success" type="submit" value="Register Account">
</form>
</div>
{% endblock %}
Login.html
{% extends 'website/dependencies.html' %}
{% load static%}
{% block content %}
<div class="container jumbotron">
<form method="POST" action="">
{% csrf_token %}
<p><input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username..."></p>
<p><input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password..." ></p>
<input class="btn btn-success" type="submit" value="Login">
<p>Do not have an account <a href='{% url 'register' %}'>Register</a></p>
</form>
</div>
{% endblock %}
Python Ecommerce Website Output
Summary
We have successfully developed python e-commerce website in just eight easy steps. In this e-commerce website we have added following functionalities: add product, place order, register, login, logout, etc. You can develop more such projects using Django. For reference, check more projects on ProjectGurukul.
waise easy code hai but isse or v acche se code likha jaa sakta tha
my website is not opening what should i do?
i get a error in navigation bar Reverse for ‘placeOrder’ with arguments ‘(”,)’ not found. 1 pattern(s) tried: [‘placeOrder/(?P[^/]+)/$’]
i have also samee issue
I want the learn the bakery website based on eCommerce
Getting NoReverseMatch at /
Reverse for ‘placeOrder’ with arguments ‘(”,)’ not found. 1 pattern(s) tried: [‘placeOrder/(?P[^/]+)/\\Z’]
exceptional error
The best website
Great Work
i get a error in navigation bar Reverse for ‘placeOrder’ with arguments ‘(”,)’ not found. 1 pattern(s) tried: [‘placeOrder/(?P[^/]+)/$’]
I get: Reverse for ‘placeOrder’ with arguments ‘(”,)’ not found. 1 pattern(s) tried: [‘placeOrder/(?P[^/]+)/$’]
Hello there:
Nice work!
I am new to both python hosting (my own server/virtual server) and django.
I had no troubles installing and using a plain django served via ubuntu/apache.
However, when I migrated the pages, I had (and still have) troubles starting the site.
I get: Reverse for ‘placeOrder’ with arguments ‘(”,)’ not found. 1 pattern(s) tried: [‘placeOrder/(?P[^/]+)/$’]
If you can help, I would appreciate.
Thanks in advance,
Laurentino
P.S. everything is clean (so I think).
bro product is not defined issue,pls fix it